News
News
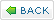
Off Grid Inverter Selection
Time:[2017-3-22] Views:3215
Modern inverters are reliable,quiet and come in a variety of sizes.This article will help demystify the inverter selection process so you can choose an inverter that is appropriate for your needs.
1.Waveform (pure sine wave and modified sine wave)
Modern off grid inverters are sold with two waveform options: sine wave and modified sine wave.Sine wave output,which has low total harmonic distortion,will power virtually any type of load,even sensitive audio electronics.Although almost all residential inverters have sine wave output,modified sine wave are more and more popular.It costs much lower than sine wave,while it may not run some types of loads satisfactorily,and some loads won’t run at all.
2.Total harmonic distortion (THD)
THD is the measure of how closely the waveform matches a perfect sine wave.Glitches,transients,harmonics,spikes,and distortion all describe alterations to the waveform shape.Inverter electronics produce steps to approximate a true sine wave—the greater the number of steps,the less THD an inverter will have.A THD of 0% is a perfect sine wave,and the larger the percentage,the farther it deviates from a sinusoidal waveform.Sine wave inverters typically show a THD of 5% or less,while the THD of modified square wave inverters may range from 10% to 40%. Because THD for modified square wave inverters varies and depends on the type of loads running,values given from manufacturers are hard to compare fairly.It is important to note that grid electricity also can have waveform distortions due to activity from all the different loads on the grid (such as large motors starting),which can cause transients in the utility waveform.
3.Rated Continuous Output Power
An off grid inverter must supply enough power to meet the needs of all the appliances running simultaneously.Before selecting an inverter,you must know the loads you will power—and their power and surge needs.
Sizing an inverter for an off grid system,which is based on instantaneous load,is very different from sizing a grid-direct inverter,which is determined by the RE power source (i.e., PV array watts). In the case of an off grid system,the inverter is usually responsible for providing energy to all the AC loads.Say you need to simultaneously power 2,000 W of AC loads.For an off grid system,you’d need an inverter that could supply at least that amount.Note that the PV array size does not enter into this inverter sizing.